Silent attrition is a behavioral challenge lurking beneath the surface in customer or member accounts; One could say this phenomenon is a result of the incredible amount of financial choices of today’s consumers, or the shift has left younger generations willing to move financial providers because of their digital banking experience. A recent research study conducted by Alkami in partnership with The Center for Generational Kinetics showed that 61% of younger Millennials (28-35) would change financial providers if another company had a much better digital banking user experience, the highest of any generation. No matter the root cause, account holders who are quietly disengaging are moving their share-of-wallet to another institution or financial services provider.
Silent Attrition = When an account holder slowly, often silently, stops engaging with a financial institution.
This means that the majority of an institution’s account holders right now, and over the next 10 years, have grown up technology dependent. Tech-dependent individuals may prefer digital interactions and often have higher expectations for seamless digital experiences. They also often prioritize convenience, efficiency, and advanced services and they may disengage if they feel their needs aren’t being met.
Addressing today and tomorrow’s account holders will require a nuanced understanding of account holder behavior and a strategic approach to engagement and retention.
48% of Millennials have been so frustrated trying to complete a digital banking task that they just gave up
Source: Alkami and The Center for Generational Kinetics Research, 2024
These tech-savvy generations demand not just convenience and efficiency but innovation in their banking services. Financial institutions face a dual challenge: mastering digital delivery and differentiating themselves in a crowded market of competition. The rise of platforms like Apple Savings underscores the appeal of a fully digital banking experience, highlighting the urgency for traditional institutions to evolve.
Let’s take the launch of Apple Card’s high-yield savings product, for example. Launched in April of 2023, when interest rates were at a historic high. They surpassed $10 billion in deposits in just a few short months. How? You could credit their strong brand value – however Apple is a technology company, not a bank. You could say it was their partnership with Goldman Sachs that made consumers feel safe. Many attribute their success to targeting a savvy, young audience looking to maximize their annual percentage yield during a time of inflation, and just as crypto was losing favor, and digital banking users were seeking new ways – Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) insured ways – to grow their nest egg.
To identify silent attrition, financial institutions must put in place a comprehensive view of account holder engagement. This involves analyzing transaction patterns, service utilization, and online interactions. By classifying account holders according to their engagement levels—from highly engaged to at-risk of attrition—banks and credit unions can pinpoint those who may silently move to another institution
There are breadcrumbs, but they are subtle. The right technology will monitor a customer or member’s transactions, such as:
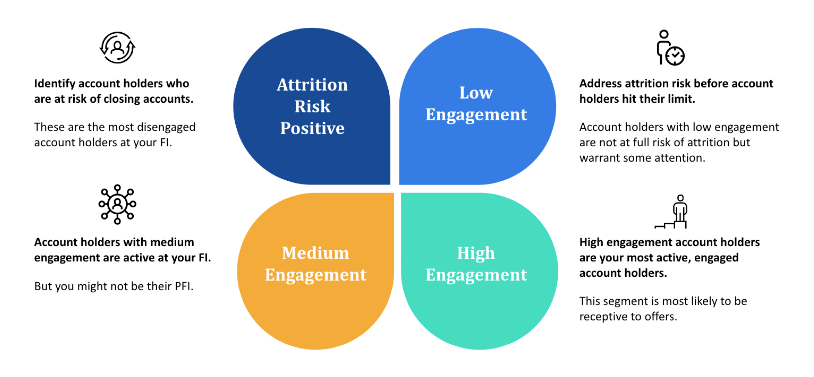
Engagement is not a one-size fits all for all credit unions and banks. Alkami has identified that it is best to break engagement into four quadrants: high engagement, medium engagement, low engagement, and attrition risk positive. And tracking how your account holders either progress or digress from one engagement tier to the next will help you understand if you are locking in the primary financial institution (PFI) status.
The simple answer to this question lies in the definition of what artificial intelligence in banking is. Artificial intelligence in banking refers to the use of machine learning algorithms, data analytics, and other intelligent systems to enhance various banking services and operations. Artificial intelligence predictive models are created by humans to solve mathematical and comprehension problems faster and more accurately than a human can do on their own.
To truly understand and enhance engagement with your customers or members, it’s essential to categorize their current level of interaction. A predictive model will assist you in monitoring even minute changes in behaviors. Which account holders are just maintaining their current level of engagement? Which are increasing? And which are decreasing it. Identifying these trends, and building audiences of those people, helps with personalized banking to inform engagement strategies.
However, simply knowing their engagement level isn’t enough. To boost engagement, you need to consider additional data points. For instance, a customer or member might show low engagement because they’ve slowed the use of their debit card, while another might not be utilizing bill pay services at all. But these observations alone don’t provide the full picture. The customer or member who is not using bill pay may be explained away, because they only have a mortgage or auto loan with your institution and do not maintain a checking account.
Understanding these specifics allows you to tailor your engagement strategies effectively. Engaging an account holder with just a loan whose engagement has remained steady differs from how you’ll engage a new account holder who is still familiarizing themselves with your services, or a long-standing account holder whose formerly consistent interactions have recently diminished.
Lastly, effective engagement requires seamless coordination between all the platforms your account holders use to interact with your institution. This includes integrating your digital banking services—both online and mobile—your website, your email delivery channel, as well as other advertising efforts. Ensuring these systems work harmoniously will provide a smoother, more responsive experience that could significantly enhance engagement.
Combatting silent attrition and enhancing account holder retention is an ongoing strategy for banks and credit unions. By integrating innovative data strategies and technologies, such as AI in banking into their practices, financial institutions can meet the evolving expectations of their account holders, ensuring a blend of efficiency, personalized banking and brand loyalty.
What is artificial intelligence in banking?
Artificial intelligence in banking refers to the use of machine learning algorithms, data analytics, predictive modeling and other intelligent systems to enhance various banking services and operations.
What is silent attrition in banking?
Silent attrition occurs when an account holder gradually stops engaging with a bank or credit union without openly expressing dissatisfaction.
Why is silent attrition a concern for banks and credit unions?
Silent attrition is concerning because it indicates unmet needs among account holders, which can lead to a decrease in customer loyalty and potential revenue loss for financial institutions. It often goes unnoticed until significant damage to the relationship has occurred.
How can financial institutions detect signs of silent attrition?
Banks and credit unions can detect silent attrition by monitoring customer insights for subtle changes in account holder behavior, such as reduced transaction frequency, decreased service utilization, cancellation of recurring payments, and less engagement with digital banking platforms.
What impact does technology have on banking engagement?
Technology plays a critical role in banking engagement, especially among younger generations who prioritize digital experiences. Institutions that fail to offer seamless, efficient, and innovative digital services may see higher rates of silent attrition among these tech-savvy account holders.
How do generational differences affect digital banking expectations?
Generational differences significantly influence banking expectations. For instance, Millennials and Gen Z have grown up in a digital-first environment and often have higher expectations for digital convenience and innovation compared to older generations like Gen X or baby boomers.
What strategies can financial institutions use to combat silent attrition?
To combat silent attrition, banks and credit unions should adopt a proactive approach by enhancing digital banking experiences, offering personalized banking services, and using AI to analyze and predict financial behaviors and needs.
How has the rise of platforms like Apple Savings affected traditional banking?
Platforms like Apple Savings have highlighted the appeal of fully mobile banking experiences, challenging traditional banks and credit unions to innovate and differentiate themselves in a crowded market. These platforms often attract younger, more digitally inclined account holders with high expectations for banking services.
What are some examples of innovative strategies to enhance account holder retention?
Innovative strategies for enhancing retention include integrating advanced analytics to understand customer and member needs, offering personalized banking products, and improving support through AI-driven tools and chatbots.
How does artificial intelligence in banking enable financial institutions to provide a personalized banking experience?
Artificial intelligence significantly enhances the banking experience by enabling personalization through deep data analysis. By examining transaction histories, account information, and interactions, financial institutions can understand individual needs and preferences. This thorough analysis allows banks and credit unions to offer customized recommendations, or predictive suggestions for financial management based on past behavior.
AI also improves customer interactions and service efficiency. Tools like AI-driven chatbots provide 24/7 assistance, adapting and improving with each interaction for more accurate responses. AI streamlines service by categorizing and addressing account holder issues efficiently, reducing wait times and boosting satisfaction. Overall, AI’s continuous learning from account holder data means personalization and service quality enhance over time, helping financial institutions strengthen their banking relationships.
